Eat vegetarian food
Being a vegetarian or even just eating less meat is one of the best things you can do for the environment. There are many reasons for it: you reduce carbon emissions, air and water pollution, excess manure problems and deforestation. If you’re a true meat lover, becoming vegetarian can even halve your total carbon emissions. Of course there are non-environmental reasons to do it too, like animal welfare, antibiotic resistance and our own health.
In the last 60 years the worldwide meat consumption has increased more than 5 times, while our individual meat consumption has almost doubled1. A return to more vegetarian / vegan food is perfectly possible, since in our history we have never eaten as much meat as we do today.
Is this EcoStep suitable for me?
If you currently eat meat and are willing to make some changes, yes. Even by just reducing the amount or type of meat you eat, you’re truly helping.
The environmental impact of meat
These are the most important reasons why it’s great to go vegetarian as much as you can:
Greenhouse gases
Meat production causes 14.5 % of humanity’s carbon emissions2, making it a huge factor for climate change. While other big factors like our transportation and energy production have to be transformed with advanced technologies and lot’s of investment, meat’s carbon emissions can simply be cut down by choosing something different to put on your plate.
In all stages of meat production greenhouse gasses are emitted:
Feed & deforestation
An average of 5 kilos of feed is needed for every kilo of meat. Because so much feed is required, it is often grown in areas where there is more land available, like the amazon. Worldwide, forests and jungles are cut down and burned every day to provide space for feed production, such as with the commonly used soy. Additionally the (artificial) fertilizer used on the land causes emissions of the even stronger greenhouse gases methane and nitrous oxide.
All this causes massive carbon emissions and destruction of nature. About 45% of the carbon emissions from meat, come from all the feed that is required2.
Methane from digestion
The digestion of the feed emits methane and nitrous oxide in ruminants such as cows and sheep, in the form of burbs, farts and manure. This accounts for about 39% of the total meat emissions2.
Transport and processing
Particulate matter
Livestock farms can cause nuisance due to particulate matter and odors in the environment. Ammonia and particles from manure, feed, feathers, skin flakes and hair are carried into the air by the wind as fine dust. This is unhealthy for people living in the area.
Manure problems
Because the feed is brought from outside to large livestock farms with many animals, there is a manure surplus: Less fertilizer is needed for the local fields and pastures than is produced. Substances from the manure such as phosphate, nitrate and ammonia can end up in the ground and surface water as a result of wind and rain. As a result, nature becomes over-fertilized and acidified, resulting in reduced biodiversity. The drinking water also needs to be purified extra to remove these substances.
The ideal solution is circular agriculture. Only local residual products from agriculture, horticulture and the food industry or grass from land not suitable for arable farming are used as feed. All manure is then used again to grow new products. However, this is only possible on a large scale if we eat less meat, otherwise the chain will not close.
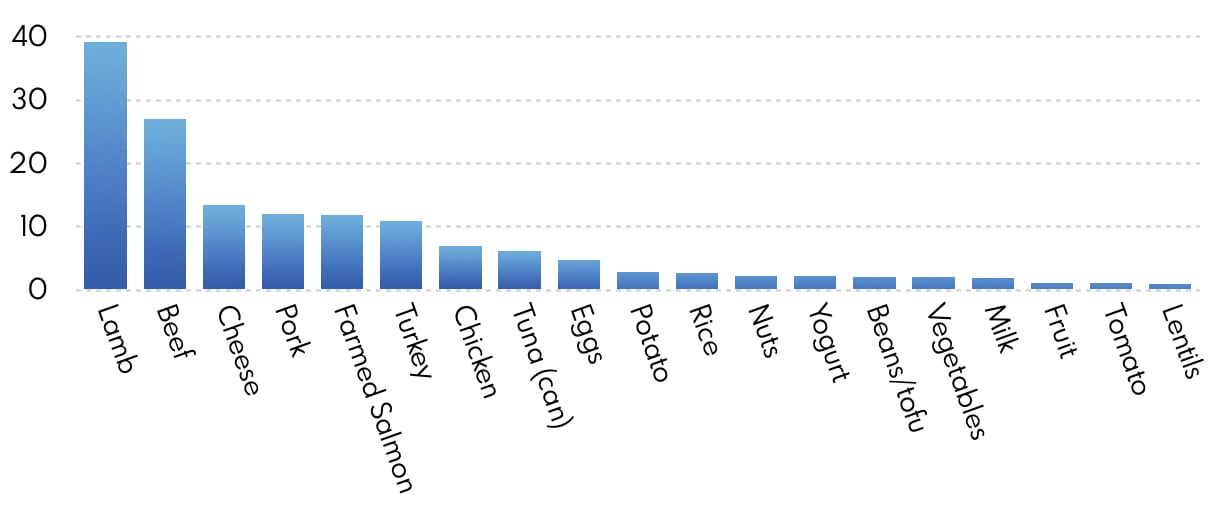
Which meat has the least impact?
While not eating meat is best for the environment, if you do eat meat, it is many times better to choose chicken than beef or lamb. In the following overview you can see the carbon emissions of different foods:
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotics have long been widely added to the feed to accelerate the growth of animals and avoid disease. This has been banned in the EU since 2006 and in the US since 2017, but it is still used against certain harmful bacteria.
When large amounts of antibiotics are used, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, such as the MRSA bacteria, develop. This is dangerous because these bacteria can no longer be treated with antibiotics and people and animals are more difficult to cure.
Animal welfare
The meat industry has taken a few steps , mostly directed by laws, to make the meat production process more humane for the animal, especially in Europe. For instance required anesthesia in case of castration and improved living space conditions. In fact, in most of Europe both hobby animals and farm animals are legally not allowed to suffer from hunger or pain. However can meat production on an industrial scale ever be truly humane?
Measures that would reduce the suffering of farm animals increase the cost, making farms less competitive. From extra living space, time outside, companionship, play, reduced growth speed, longer lifespans, better food, it all costs extra money. Making it either impossible to be competitive or making the price of meat extremely high if these measures are made mandatory. And in the end, the animal will always have to be taken to the slaughterhouse.
Additionally, large scale meat production increases the likelihood, spread and impact of (new) epidemics, like bird flu and foot-and-mouth disease 3. In case this happens, usually the entire group of animals will be put to death. It increases the chances of new diseases cropping up that could also affect humans as well.
If you still want to eat meat and care about animal welfare, organic meat is usually produced under slightly more animal-friendly conditions.
Organic meat
Organic meat mainly improves animal welfare, because the animals can go outside all year round, they have more space inside and are generally a lot healthier. It’s better for the environment in some ways, but worse in others. Because the animals live longer and get more food and space, organic meat is about one and a half times more expensive in the store, depending on the type of animal.
Better for the environment
No artificial fertilizers or synthetic crop protection agents are used in the production of organic meat. The feed also has a lower environmental impact per kg because it comes more from the surrounding farms and less from distant countries. All this ensures better soil quality, less deforestation in distant countries and a better environment.
Worse for the environment
However, there are also reasons why organic meat is worse for the environment. Organic animals live longer, requiring more feed, producing more manure surpluses and emitting more greenhouse gases.
Recognize organic meat
You can recognize organic meat in the EU by the ‘green leaf of stars’, which is the European quality mark for organic farming. In order to receive this quality mark, the meat must meet the strict requirements of the EU. There is also the Demeter quality mark for biodynamic agriculture based on anthroposophical principles. In the United States they use the USDA label.



Meat Substitutes
Plant-based meat substitutes are much better for the environment than meat and contain protein as well. Its production emits much less greenhouse gases and requires less energy, land, fertilizer and water.
What are the best meat substitutes?
Legumes, nuts, quorn, tofu, tempeh and vegetable ready-to-use meat substitutes based on soy, grain, vegetables, seaweed or fungi are the most environmentally friendly meat substitutes. However, dairy-based meat substitutes, such as Valess, for example, are comparable to chicken in terms of environmental impact. Cheese is even worse.
Check the packaging to see what is in your meat substitute. Is it plant based? Then you’re fine.
How to make the shift to be a vegetarian
For some, reading this might already be enough to become a vegetarian today. But for many it might be more suitable to get there in steps. Maybe you first don’t eat meat every other day. Then only during the weekend. Then only once a week. This way you get adjusted to it and before you know it, you’re a vegetarian too.
Extra tips
Learn to cook some new vegetarian dishes, instead of only substituting the meat in the dishes you knew from before. There are many great vegetarian cookbooks and recipes online. This way you discover new flavors and won’t miss the meat much.
Watch a few documentaries on the meat industry, it’s quite upsetting what goes on there. Seeing this can provide you with the extra emotional push to make the change.
Realize that the change to a vegetarian diet gets easier the longer you stick with it. Your brain needs some time to get used to a new habit, but in the long run it’s easy.
PLANT TREES AND BECOME CARBON NEUTRAL TODAY
Planting trees and reducing your carbon emissions is essential for the climate, biodiversity and healthy living conditions. With the trees we plant in Tanzania and our EcoSteps you can easily do both and tackle climate change beautifully, effectively and completely. So start today: